What is Debounce ?
Table of Contents
Introduction
In an online tech news feed, someone posted a simplified note-taking web app implemented fully on the client side using html and javascript. The javascript included a function for performaing debounce. In the comments, many folks were ignorant of what a debounce is meant to achive and were surprised discovering the technique for the first time (Check Google Trends on how far back they go!) . Even the original poster seem to be surprised by it.
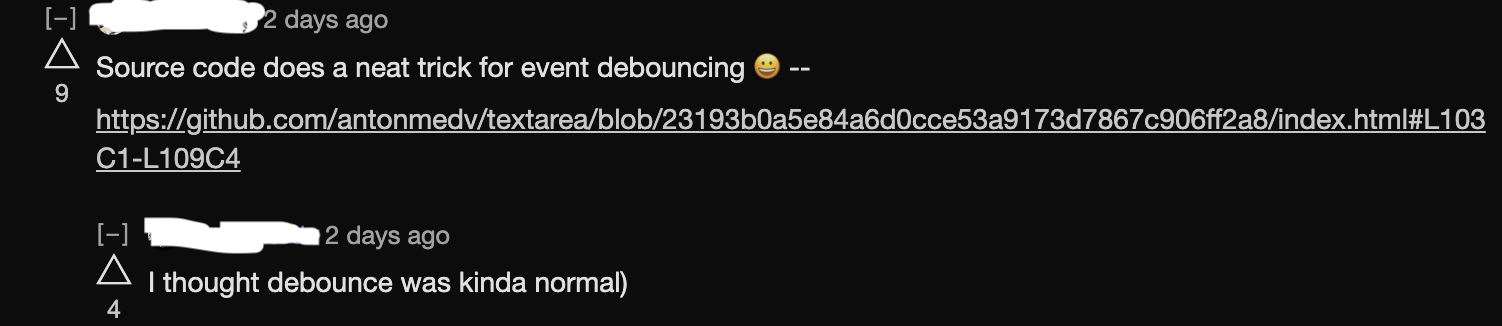
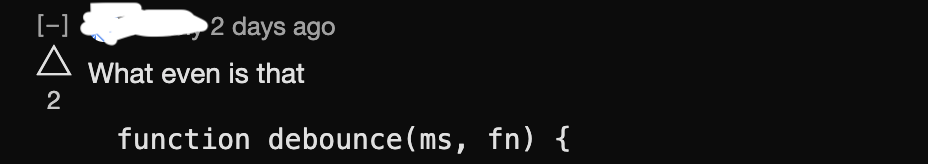
I will give a code walkthrough of debounce and explain its use-case.
Code
I have copied only the relevant bit here and numbered explanation follow down below:
//... more code
<article contenteditable="plaintext-only" spellcheck></article> // 1
<script>
const article = document.querySelector('article') // 2
article.addEventListener('input', debounce(500, save)) // 3
//... more code
function debounce(ms, fn) {
let timer // 4
return (...args) => { // 5
clearTimeout(timer) // 6
timer = setTimeout(() => fn(...args), ms) // 7
}
}
</script>-
The html tag (
article) for a text area to enter text content. This will be the place to enter the note as input. -
The html tag (
article) is programmatically referenced via javascript. -
A function (
debounce) is executed immediately and the return value (another anonymous function that satisfies event listener type) is set as the event listener and attached to the article tag which will be invoked whenever aninputevent is triggered on the tag.debouncetakes 2 parameters - timeout in milliseconds and another function (save) to invoke after the timeout expires. -
debouncedeclare atimervariable which is referred inside the anonymous function and persist as part of the environment of anonymous function long afterdebouncehas finished executing. This concept is calledclosurein programming language parlance. -
debouncereturn an anonymous function (actual event listener) that takes in all the args passed to it by javascript environment (browser in this case) when an event is triggered. -
The
timervariable is cleared - This effectively cancel any future invocation ofsetTimeoutcallback function. -
The
timervariable holds the return reference to thesetTimeoutcallback registration. The callback is invoked aftermstime has passed and it invokes the originalfnpassed todebouncewhich in this case issavefunction - passing all the parameters passed to a event listener wheninputevent is triggered.
Summary of the code
Debounce make sure, an event listener is only invoked when:
-
mstime has passed after the event, and -
There are no new event during
mswait time. -
If there is a new event within
mswait time, the wait time is reset again, and we go to step 1.
Debounce vs Throttle
While debounce make sure specific amount of time is elapsed since the last time the event is invoked, throttle guarantee that an event is invoked atmost only once within a specific amount of time. The implementation of throttle is left as an exercise to the reader.
Clue: You can implement throttle using setTimeout and a boolean flag.